| April 21, 2021 |
The new PC-3000 Flash Software Ver. 7.5.11 is available! |

The PC-3000 Flash is a top-notch solution to recover data from most of existing NAND Flash devices. It is acknowledged worldwide as the most comprehensive tool for the easiest and smartest NAND Flash data recovery.
For you to recover most cases ever possible, developers continuously add new features to the PC-3000 Flash. Enhanced translator algorithms and solutions for SanDisk data recovery, BUS pinout detection for the Spider Board adapter, the support of new microschemes, a specialized method for data analysis and image building for the FAT32 based file systems – all this and much more is now available with the latest English, Japanese, Korean and Chinese software update:
- PC-3000 Flash software Ver. 7.5.11
All authorized PC-3000 Flash technical support users will get the latest PC-3000 Flash software version in the Personal Update Boxes. If you have any questions, feel free to address them to our Technical Support.
Please contact us to learn more on how to become an authorized technical support user and receive all of the recent PC-3000 Software Updates:
RENEW YOUR TECHNICAL
SUPPORT CONTRACT
A SHORT LIST OF THE MAIN ENHANCEMENTS
| ENHANCED | SanDisk 8Sec translator for TLC memory algorithm |
| ADDED | SanDisk 8Sec translator for MLC memory |
| ADDED | assembly translator algorithm for SM3268 / SM3269 based drives |
| ENHANCED | SM2704 Translator Algorithm |
| ENHANCED | SSS6677 Translator Algorithm. Now the assembling algorithm can search the damaged copies of translator tables and reconstruct a working copy from the partially working tables |
| ENHANCED | PS8210 Translator Algorithm |
| ADDED | support for NAND QLC Intel / Micron N18 chips |
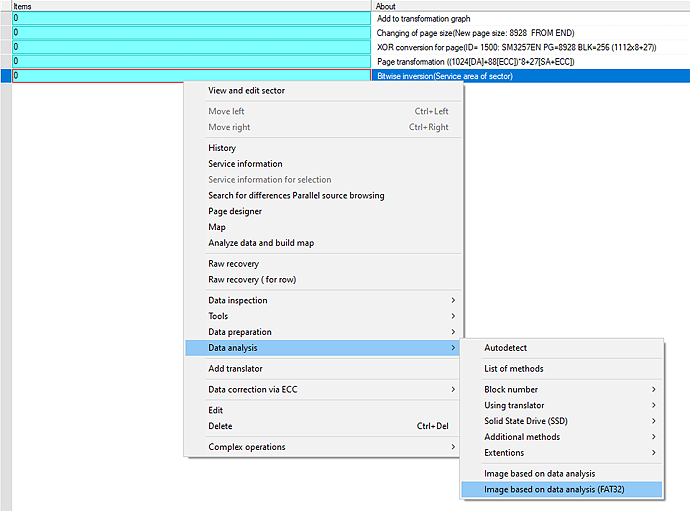
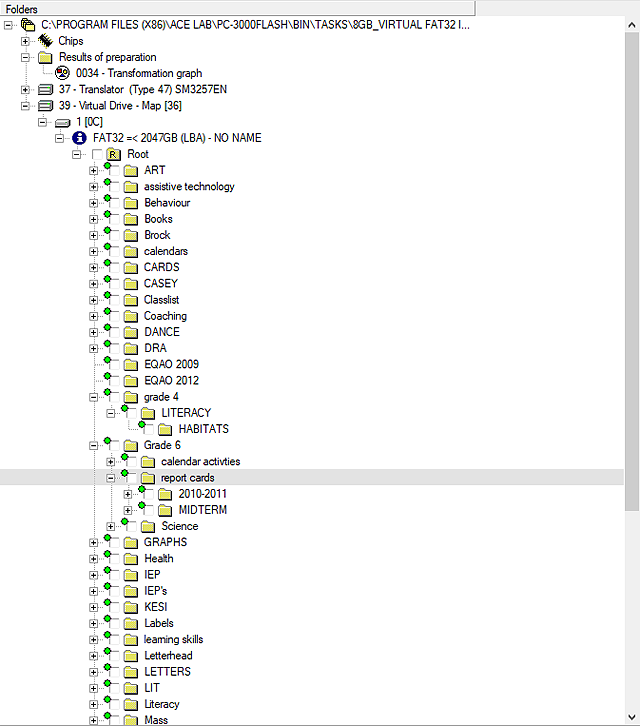
| ADDED | a specialized method for data analysis and image building for FAT32-based file systems: “Image based on analysis (FAT32)” |
| ADDED | BUS pinout detection for the Spider Board adapter. |
A DETAILED LIST OF ENHANCEMENTS:
| ENHANCED | SanDisk 8Sec translator for TLC memory algorithm:
|
| ENHANCED | SanDisk TLC translator to work with drives that have offsets in the SLC block |
| ADDED | SanDisk 8Sec translator for MLC memory:
|
| ADDED | the ability to detect the shift of the ROOT folder in the expected place for Sandisk MLC / TLC image building algorithms. Information about the possible shift will be displayed in the log |
| ENHANCED | image assembling digitalization of the log in Sandisk MLC and TLC translators |
| ADDED | assembling translator algorithm for SM3268 / SM3269 based drives |
| ENHANCED | SM2704 Translator Algorithm |
| ENHANCED | SSS6677 Translator Algorithm. Now the assembling algorithm can search the damaged copies of translator tables and reconstruct a working copy from the partially working tables |
| ENHANCED | PS8210 Translator Algorithm |
| ADDED | support for NAND QLC Intel / Micron N18 chips:
|
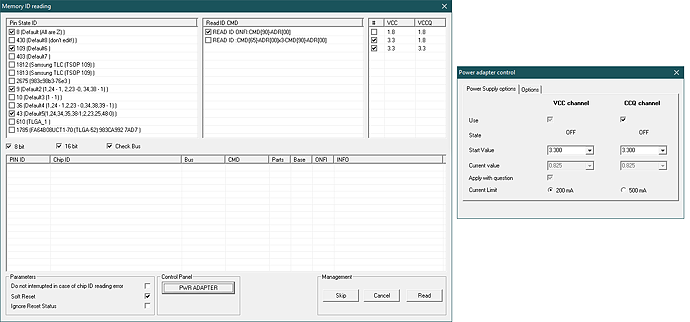
| ADDED | the new feature of voltage control in the ID reading mode . Now it is possible to read the ID with 1.8V and 3.3V for VCC and VCCq circuits. It helps to read the new 1.8V NAND chips by default without the necessity to change the power parameters in the PC-3000 Flash Power Control Adapter settings |
| ADDED | a new algorithm of marker parameters detection for image building by Block Number Type 1 [0000]. It helps to detect the correct mask parameters for different cases |
| ADDED | a specialized method for data analysis and image building for FAT32-based file systems: “Image based on analysis (FAT32)” |
This method, based on deep analysis of FAT structures, in some cases allows you to get a high-quality logical image. The method turns out to be irreplaceable in tasks where there is no translator algorithm for image building or there is no marker in SA area (FC1178/79, SSS6696, SSS6697, SSS6698, TC58NC6623, CBM2199a and other noname controllers). You can learn more about this method in our article
| ADDED | BUS pinout detection for the Spider Board adapter. This new feature allows to detect the pins of I/O data lines in case if those pins were unknown. You can read more about this in our article |
| ENHANCED | the “Visual cutting of sectors in a block” tool. Added auto-detection of clipping formula and group clipping of selected pages by pressing the [Space] key |
| ADDED | support for basic read commands with a 4-byte block address. This allows you to read large-capacity chips where the block addressing goes beyond 3 bytes |
| ADDED | the ability to enter values in the hexadecimal form to the dialog for editing the channel synchronization table. A flag that allows you to apply the entered value immediately after entering has been added as well |
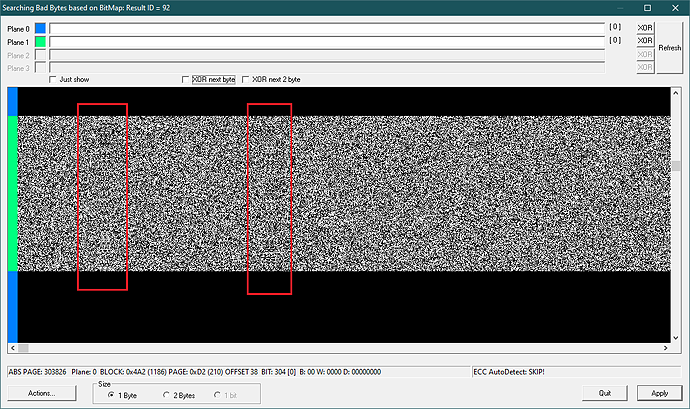
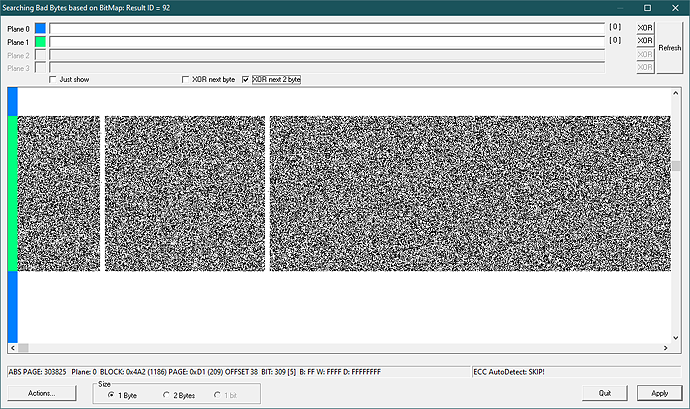
| ADDED | an additional “XOR Next 2 Byte” flag in the mode of deleting Bad Bytes by BitMap. It is useful when working with dumps of AlcorMicro controllers |
| ADDED | the ability to show on the screen the voltage control dialog of the supply circuits simultaneously with Reading the ID of NAND chips. That allows you to control the supply voltage directly in the process of reading the identifier |
| ADDED | output to the protocol in the reread mode based on external files. That allows you to evaluate which file is applied for each range |
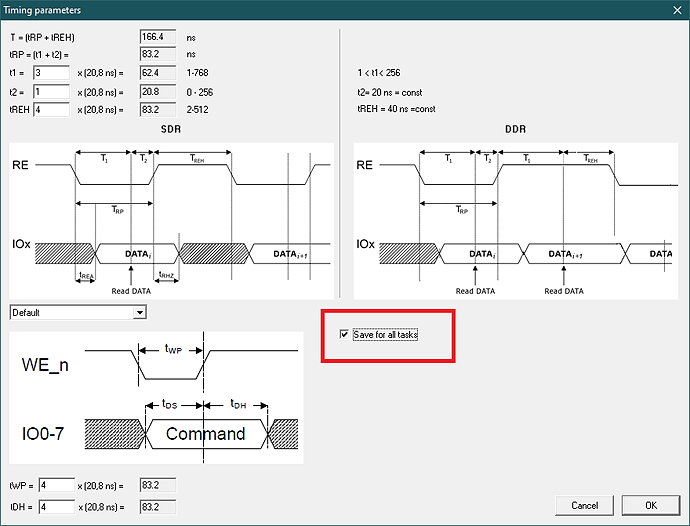
| ADDED | a flag to the dialog for editing the protocol time parameters. That allows to save the specified values not only for the current task, but also as initial values for all subsequent tasks |
| ADDED | Resources:
|