The Data Extractor SAS is a professional data recovery software solution functioning in tandem with the PC-3000 SAS hardware-software product. It is intended for recovering data from damaged SAS (Serial Attached SCSI), SCSI, USB HDD, SSHD (Solid State Hybrid Drive) HDDs.
- Data Extractor SAS can work with a variety of file systems such as FAT, exFAT, NTFS, HFS+, APFS, EXT2/3/4, XFS, ReiserFS, BtrFS, VMFS, UFS1/2, ZFS, DHF4.1, WFS0.x
- VMDK (VMWare), VHD, VHDX, DMG images are supported
- Data Extractor SAS has modes used in forensic investigations
The Data Extractor SAS is capable of working with 4 HDDs simultaneously. Drives can be connected to the PC-3000 SAS ports, motherboard ports, special controllers (xSATA, xUSB, xSCSI, xSA etc.) or represented as HDD images.
The PC-3000 SAS allows you to repair physically damaged HDD drives in technological mode and gain access to data. All ports are separable and independent. Performance slowdown is minimal even when all ports are in use at the same time.
Using the Data Extractor SAS, you can create full (sector-by-sector) or partial data copies from the damaged drive to good drives connected to the PC-3000 SAS ports, motherboard and also to image-files.
Recovering data with the Data Extractor SAS
There are three types of causes of HDD malfunction: physical damage, logical damage, and a combination of physical and logical damage.
Physically damaged HDDs:
Physically damaged HDDs are hard drives with damaged surfaces, damaged magnetic-head assembly, defective "service information" that leads to unstable reading and multiple errors, and/or a corrupted translation system between logical block addressing (LBA) and physical geometry of HDD (translator). This can be caused by:
- BAD sectors caused by damaged surfaces or a malfunction of the magnetic head assembly (MHA)
- "knocking" sounds, which may be caused by corruption of servo labels or an MHA malfunction
- Service information destruction
- System violation of LBA - PCHS translation
- unstable reading caused by re-installation of MHA or disk pack
- data recovery after HOT-SWAP procedure
Logically damaged HDDs:
Logically damaged HDDs are hard drives with damaged logical structures which prevents access to the user information via OS instruments.
This can be caused by:
- damaged partition information (MBR, GPT, APS, etc.)
- slight damage to file system metadata caused by HDD or OS failures
- deleted folders and files
- significant damage to data and metadata caused by formatting
- logical damage caused by viruses
Combination of physical and logical damage:
You can use the wide range of functions of the Data Extractor UDMA to handle various types of data recovery cases, including those that have both physical and logical damage.
Data recovery from physically damaged HDDs
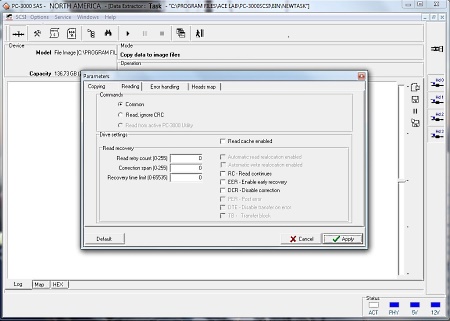
It is very important to read the maximum data volume possible in the shortest period of time, as a damaged HDD can stop functioning at any time. The Data Extractor SAS has integrated functionality for logical analysis of file systems which allows for reading of only necessary data. This technology greatly reduces the volume of read data, the duty cycle of damaged HDDs, and the time required for data recovery.
The Data Extractor SAS has extended functionality for HDD reading:
- reading by head map
- management of hardware level data recovery parameters while reading
- read ahead (cash function) disabling
- reading with ignoring ECC
- read forward and backward
- reading by used/unused sectors map
- power supply control
- software and hardware resets
The "Create virtual translator" option enables recovery of data from an HDD with a corrupted dynamic translator. File system metadata and user data are used in this mode.
Data recovery from logically damaged HDDs
There are some special modes for recovering data from logically damaged HDDs:
- "Explorer" mode – to get access to the damaged partitions, folders and files
- "Raw recovery" mode – to recover data when file system structures are catastrophically damaged
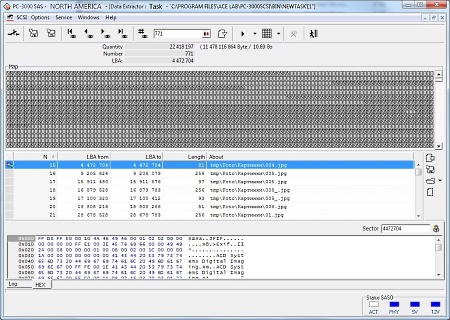
- "Object map" mode – to work with fragmented structures (reading, copy creation etc)
- "Quick disk analysis" mode – to solve cases with damaged information about partitions
- "Partition data analysis" and other special modes for each file system – to recover data from specific damaged file system (including data deleted by users)
- Modes for viewing and editing metadata in various file systems
- Building maps of used/unused sectors, metadata and file system data
- "Edit map of virtial drive" - this mode allows to recover virtual drives with lost allocation information
Using Data Extractor SAS for forensic purposes
Data Extractor SAS has special modes used by forensic investigators:
- hash sum calculation for MD5 and SHA1
- exporting catalogs list and files into csv format
- building various maps: disk maps, used/unused sectors maps, file system metadata maps etc
- changing/resetting to factory value of MaxLBA HDD
- HDD mounting in "read-only" mode
- HDD data copy creation with writing to several recipients
- Reading and export in .E01, .AFF, .S01, .DEFF formats are supported. DEFF stands for Data Extractor Forensic Format - the PC-3000 proprientary format with checksums and compression
| PC-3000 SAS |  |
Data Extractor SAS |