The Data Extractor SAS RAID Edition is a specialized software product intended for recovering data from RAID storage devices. Functioning in tandem with the PC-3000 SAS hardware-software product, it forms the PC-3000 SAS RAID Professional System.
- The Data Extractor SAS RAID Edition includes all the features of Data Extractor SAS;
- A wide range of supported levels is provided:
- "simple" RAID levels: 0 (Stripe), 1 (Mirror), JBOD, 1E Offset, 1E Adjacent, 4, 5, 5E, 5EE, 6, 6 Adaptec
- Combined levels: 10, 50, 60, 51, etc. due to the possibility to create RAID from RAID
- Tabular presentation enables to define optional configurations.
- WSS (Windows Storage Spaces) ZFS RAID-Z, BtrFS RAID, Apple Fusion Drive (HFS+, APFS)
- Restoring the software RAID and NAS
- A wide variety of RAID members are supported:
- Up to four damaged HDDs connected to the PC-3000 SAS ports
- Storage devices connected in standard way (including SCSI and SAS)
- Image-files
- Data Extractor tasks created earlier with copies to files
- Previously created virtual RAIDs.
- Drives connected to the PC-3000 Express ports (if both systems are plugged into one computer)
- Advanced features for operations with damaged drives within a RAID
- Unique modes of automatic and interactive detection for RAID configurations
- Software emulation of RAID controller:
- Mounting of virtual RAID to the Operating System
- High read speed (approximately 1.3 GB/sec for a Stripe of 4 SSDs connected to the PC-3000 SAS ports)
- Recovering data from redundant arrays
The main problems with RAID recovery
Today, RAID arrays have a large number of drives and have complicated structures (combined and proprietary levels) while several members of a RAID can have serious physical damage (damaged surfaces, HSA, servo-information, etc.). The file system metadata of the RAID can be also damaged.
Thus, there are several problems with RAID data recovery:
- Working with the damaged HDDs in the RAID
- Defining the array configuration
- Array assembly and logical recovery of data from it
These problems may also occur simultaneously. The Data Extractor SAS RAID Edition is a professional tool providing a wide range of features addressing all major problems completely.
How to work with damaged HDDs in a RAID
The Data Extractor SAS RAID Edition can work with four damaged HDDs connected to PC-3000 SAS ports within one task at the same time. The total number of the connected HDDs can be increased using motherboard ports and image files.
Crucial features for working with damaged HDDs of a virtual RAID:
- Ability to make a full or partial data copy from any HDD included in the RAID
- Ability to define and use a virtual translator for any HDD in the RAID or the whole virtual RAID
- Ability to manage and interact with the specialized PC-3000 SAS utility for HDDs connected to the PC-3000 SAS ports (power supply management, reset commands, choice of reading command etc.)
- Advanced features for working with SCSI and SAS storage devices (full control over reading parameters, choice of reading command, building the head map etc.)
- Ability to skip the damaged HDD while defining the array configuration or to use data taken from a copy
- Redundancy usage with the purpose of data recovery from the problematic HDDs
- Integrated logical analysis features that allow reading only the minimally necessary amount of data from the storage device, thus reducing the load and increasing the chances of successful recovery
Before the Data Extractor RAID Edition appeared, you would have had to have made a full sector-by-sector copy of the data from a simple stripe if one of its members was physically damaged and could not be connected in a standard way, or it would not have been possible to get access to its sectors without using the PC-3000 SAS methods. You could only have attempted to recover the user data after creating a copy.
Taking into account the significant capacity of high end HDDs and possible issues with a full copy of the damaged drive, the Data Extractor SAS RAID Edition provides a unique approach:
- Create a Virtual RAID.
- Open the Virtual RAID in the Data Extractor Explorer and get an understanding of the data organization in the virtual RAID.
- Build a map of the required data. It can be a map of used sectors, a data map of the required catalogs, a necessary file map, or a metadata map.
- For the built map, build a “Sub-map” of sectors to be read from the damaged HDD.
- Make a sector-by-sector copy only of these required sectors by using the Data Extractor.
- Save the required data.
How to define the array configuration
RAID configurations can be very complex and data recovery from RAID is not easy even if the configuration appears to be simple. It can be difficult to define the correct order of HDDs, the block size and the initial shift. The task may be complicated further by drive damage or user attempts to rebuild the array.
Key features of the Data Extractor RAID Edition for defining the array configuration:
- Unique auto-detection mode for a wide range of popular configurations. This mode is based on the analysis of file systems and user data
- Powerful interactive mode that allows for easily defining unusual configurations, and very flexible automatic operations with an ability to control the current result
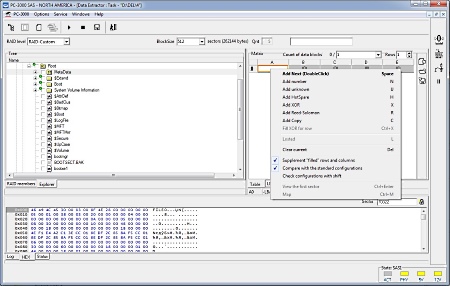
- Useful search tools help define numerous RAID parameters including detecting the size and reviewing the file system structures, metadata with disk structure (MBR, GPT etc.), including the metadata with the virtual RAID organization (mdadm RAID superblock), and analysis of the information from LDM
- Array parameters can be defined without touching defective HDDs
- "RAID member statistics", this mode allows to reliably and clearly detect basic RAID parameters: block size, level of array, number of members, delay
How to assemble a RAID and logically recover data
Even if you know the full configuration of a RAID and there are no problems with the damaged HDDs, recovering data from a RAID can be a complicated task for multiple reasons: a large number of drives which need to be connected simultaneously, slow read speeds, impossibility to assemble an unusual array configuration, or logical damage.
Advantages of the Data Extractor SAS RAID Edition:- You can connect up to 4 HDDs to the PC-3000 SAS ports in addition to the local motherboard ports
- High read speed from the virtual RAID (the speed is in excess of 1.3 GB/sec for a stripe with 4 SSDs connected to the PC-3000 SAS ports)
- Extended list of standard RAID levels with the possibility of defining new unknown levels
- Ability to recover and check the integrity of data for arrays with redundancy
- All logical recovery modes can be used for the virtual RAID
- Map building can be done by taking into account the map position of a specific RAID member. You can choose the specific sectors for a file map or RAID partition.
| PC-3000 SAS |  |
Data Extractor SAS
Data Extractor SAS RAID Edition |